KUALA LUMPUR – Malaysia is facing a concerning situation on two fronts: a surge in personal data breaches and an overwhelming amount of electronic waste. Recent reports highlight the severity of these issues, raising questions about cybersecurity measures and waste management practices in the country.
Data Breaches at Alarming Rates
In 2024, Malaysia recorded the highest rate of personal data leaks among key Asian markets. This alarming statistic exposes the vulnerability of citizens' personal information and raises serious concerns about the effectiveness of cybersecurity protocols. The implications of these data breaches can be far-reaching, affecting individuals' privacy, financial security, and overall trust in online systems.
Experts are urging for increased investment in cybersecurity infrastructure, stricter enforcement of data protection laws, and greater public awareness to mitigate the risk of future breaches. "The government and private sector need to work together to strengthen our defenses against cyber threats," says one cybersecurity analyst. "Protecting personal data is not just a matter of compliance; it's a matter of national security."
The Growing E-Waste Mountain
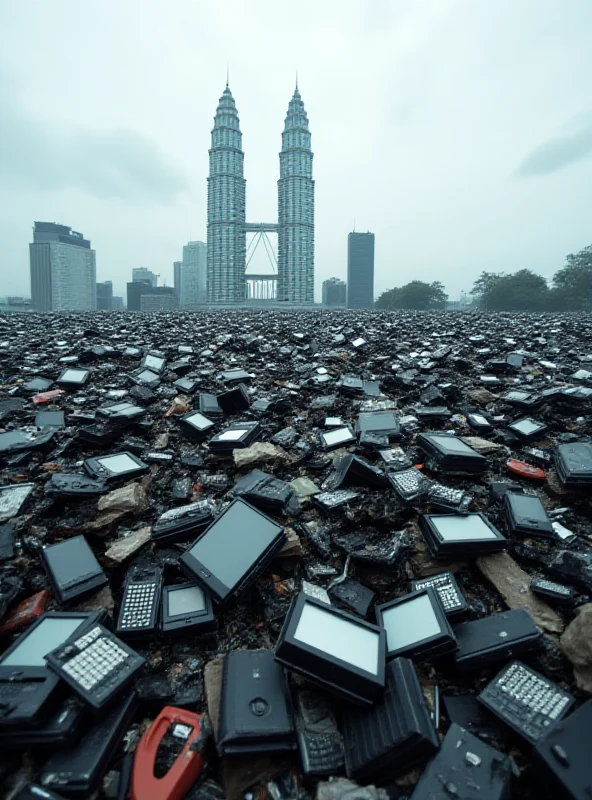
Adding to the challenges, Malaysia is also grappling with a massive amount of electronic waste. Over the past 19 years, the country has generated an estimated 2.62 million metric tonnes of e-waste. To put that into perspective, that's enough to fill nearly three-quarters of the iconic Petronas Twin Towers.
This staggering volume of discarded electronics poses significant environmental and public health risks. E-waste contains hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can leach into the soil and water, contaminating ecosystems and endangering human health. Improper disposal methods, such as open burning and landfilling, exacerbate these risks.

What Can Be Done?
Addressing the e-waste crisis requires a multi-pronged approach. Stricter regulations on e-waste disposal, promotion of responsible recycling practices, and public awareness campaigns are crucial steps. Furthermore, manufacturers need to adopt eco-design principles to create more durable and recyclable products.
Initiatives like extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, where manufacturers are responsible for the end-of-life management of their products, can incentivize better design and recycling practices. Consumers also have a role to play by properly disposing of their old electronics and supporting responsible recyclers.

Malaysia's ability to effectively manage these challenges will be crucial for ensuring a secure and sustainable future. By strengthening cybersecurity measures and implementing comprehensive e-waste management strategies, the country can protect its citizens and its environment.
“Addressing the e-waste crisis requires a multi-pronged approach. Stricter regulations on e-waste disposal, promotion of responsible recycling practices, and public awareness campaigns are crucial steps.”
The dual challenges of data breaches and e-waste highlight the urgent need for proactive measures and collaboration across all sectors of society. Only through concerted efforts can Malaysia overcome these hurdles and build a more resilient and sustainable future.
